Inconel 625 and Inconel 825 are both nickel-based alloys widely used in corrosive and high-temperature industrial environments. Although they share some similarities in corrosion resistance and nickel content, they are designed for different service conditions and mechanical requirements. Understanding the differences between Inconel 625 and Inconel 825 is critical for selecting the right material for applications in oil and gas, chemical processing, marine engineering, and power generation.
Basic Alloy Classification
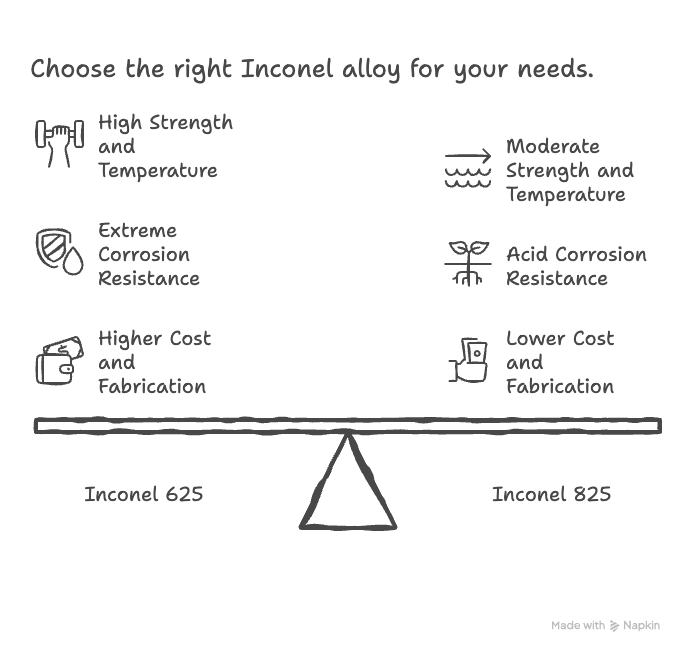
Inconel 625 is a solid-solution strengthened nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy with niobium added for enhanced strength. It is classified as a high-strength nickel alloy suitable for extreme mechanical and thermal conditions.
Inconel 825 is a nickel-iron-chromium alloy with additions of molybdenum, copper, and titanium. It is primarily designed for corrosion resistance rather than high mechanical strength.
Chemical Composition Comparison
| Element | Inconel 625 | Inconel 825 |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | ≥ 58% | 38 – 46% |
| Chromium (Cr) | 20 – 23% | 19.5 – 23.5% |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 8 – 10% | 2.5 – 3.5% |
| Niobium (Nb) | 3.15 – 4.15% | — |
| Iron (Fe) | ≤ 5% | ≥ 22% |
| Copper (Cu) | — | 1.5 – 3% |
| Titanium (Ti) | — | 0.6 – 1.2% |
The higher nickel, molybdenum, and niobium content in Inconel 625 directly contributes to its superior strength and resistance to extreme environments.
Mechanical Properties
Inconel 625 offers excellent mechanical strength across a wide temperature range, including cryogenic and elevated temperatures. It maintains high tensile and yield strength without requiring precipitation hardening.
Inconel 825 provides moderate strength but is not intended for high-stress structural applications. Its strength is closer to that of corrosion-resistant stainless steels.
| Property | Inconel 625 | Inconel 825 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Very High | Moderate |
| Yield Strength | High | Lower |
| High-Temperature Strength | Excellent | Limited |
Corrosion Resistance
Inconel 625 exhibits outstanding resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, oxidation, and chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking. It performs well in seawater, acidic environments, and high-temperature oxidizing conditions.
Inconel 825 is specifically engineered for resistance to sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, nitric acid, and alkaline solutions. The copper addition significantly improves resistance to reducing acids.
Temperature Resistance
Inconel 625 can operate reliably at temperatures up to approximately 980°C, maintaining strength and oxidation resistance.
Inconel 825 is typically used at lower temperatures, generally below 540°C, where corrosion resistance is the primary concern.
Fabrication and Weldability
Inconel 625 has good weldability but is more difficult to machine due to its high strength and work-hardening behavior.
Inconel 825 is easier to fabricate, machine, and form, making it a cost-effective choice for complex corrosion-resistant systems.
Typical Applications
Inconel 625 Applications:
Used in aerospace components, offshore platforms, subsea piping, heat exchangers, gas turbine parts, high-pressure piping, and nuclear industry equipment.
Inconel 825 Applications:
Commonly used in chemical processing equipment, acid production plants, pickling equipment, pollution control systems, and oil & gas sour service environments.
Cost Comparison
Inconel 625 is significantly more expensive due to its higher nickel content, alloying elements, and mechanical performance.
Inconel 825 offers a more economical solution when corrosion resistance is required without extreme mechanical loads.
How to Choose Between Inconel 625 and 825
Choose Inconel 625 if: high strength, high temperature performance, and extreme corrosion resistance are required.
Choose Inconel 825 if: corrosion resistance in acidic or chemical environments is the main requirement and mechanical loads are moderate.
Related Questions
Is Inconel 625 stronger than Inconel 825?
Yes, Inconel 625 has significantly higher tensile and yield strength than Inconel 825.
Which alloy is better for sulfuric acid environments?
Inconel 825 performs better in sulfuric acid due to its copper content.
Is Inconel 825 a substitute for Inconel 625?
No, Inconel 825 cannot replace Inconel 625 in high-temperature or high-stress applications.



