Hastelloy C276 and Inconel 625 are two of the most widely used nickel-based superalloys in harsh industrial environments.
Although both materials offer exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance, they differ in chemical
composition, mechanical properties, cost, and ideal application scenarios. This article provides a clear and structured
comparison of Hastelloy C276 vs Inconel 625, using detailed tables, technical breakdowns, and easy-to-understand explanations
to help buyers, engineers, and procurement specialists choose the appropriate alloy.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Hastelloy C276 contains higher molybdenum and tungsten, giving it stronger resistance to aggressive reducing media.
Inconel 625 contains more niobium, enhancing high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance.
| Element | Hastelloy C276 (%) | Inconel 625 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | Rem. | 58 min |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 15–17 | 8–10 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 14.5–16.5 | 20–23 |
| Tungsten (W) | 3–4.5 | — |
| Iron (Fe) | 4–7 | 5 max |
| Niobium + Tantalum (Nb+Ta) | — | 3.15–4.15 |
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
C276 is widely considered one of the most corrosion-resistant alloys available, especially in highly reducing,
acidic, and chloride-rich environments. In contrast, Inconel 625 performs excellently in oxidizing and moderately corrosive environments but is not as strong as C276 in strong reducing acids.
| Environment | Hastelloy C276 | Inconel 625 |
|---|---|---|
| Reducing acids (HCl, H2SO4) | Excellent | Moderate–Good |
| Oxidizing acids (HNO3) | Excellent | Excellent |
| Seawater pitting resistance | Excellent | Very Good |
| Stress corrosion cracking | Outstanding | Good |
| Mixed acid environments | Superior | Good |
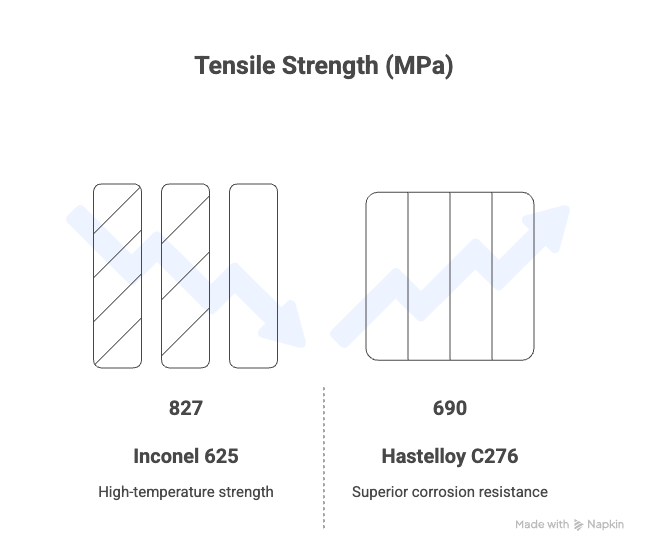
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Both alloys deliver strong mechanical strength, but Inconel 625 shows better high-temperature performance due to Nb strengthening.
| Property | Hastelloy C276 | Inconel 625 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 690 | 827 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 283 | 414 |
| Elongation (%) | 61 | 30 |
| Max Service Temperature | ~1100°C | ~980–1100°C |
Key Technical Differences
1. Corrosion resistance: C276 is superior in nearly all harsh chemical environments.
2. Strength: 625 is stronger at high temperatures because of Nb stabilization.
3. Price: C276 is generally more expensive due to higher Mo and W content.
4. Applications: C276 is preferred for chemical processing, while 625 is used in aerospace, marine, and high-temperature systems.
Applications Comparison
| Industry | Hastelloy C276 Typical Use | Inconel 625 Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Reactors, acid tanks, pickling equipment | Heat exchangers, scrubbers |
| Oil & Gas | Sour gas applications, pipelines | Downhole equipment, flexible risers |
| Marine | Seawater handling components | Marine exhausts, seawater piping |
| Aerospace | Corrosive chemical resistance | Jet engines, turbine components |
| Pollution Control | Flue gas scrubbers | Air-handling systems |
Which Alloy Should You Choose?
Choose Hastelloy C276 if your environment involves aggressive, reducing, or chloride-loaded acids.
Choose Inconel 625 if you need high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance with good corrosion performance at a lower cost.
Related Questions
Is Hastelloy C276 more corrosion-resistant than Inconel 625?
Yes. C276 offers superior resistance in reducing acids, chloride environments, and mixed industrial chemicals.
Which alloy is cheaper, C276 or 625?
Inconel 625 is generally cheaper because C276 contains more expensive elements like molybdenum and tungsten.
Can Hastelloy C276 and Inconel 625 be used at high temperatures?
Both can operate above 900°C, but Inconel 625 provides better high-temperature mechanical strength due to niobium strengthening.



