Hastelloy X and Inconel 625 are two high-performance nickel-based superalloys engineered for extreme environments. Both alloys provide excellent high-temperature strength, oxidation resistance, and corrosion resistance, but their composition and typical applications differ. Hastelloy X excels in resisting oxidation and hot corrosion in severe chemical environments, while Inconel 625 combines high mechanical strength with superior resistance to chloride stress corrosion. Comparing these alloys helps engineers and designers choose the optimal material for aerospace, power generation, chemical processing, and marine applications.
Chemical Composition Comparison
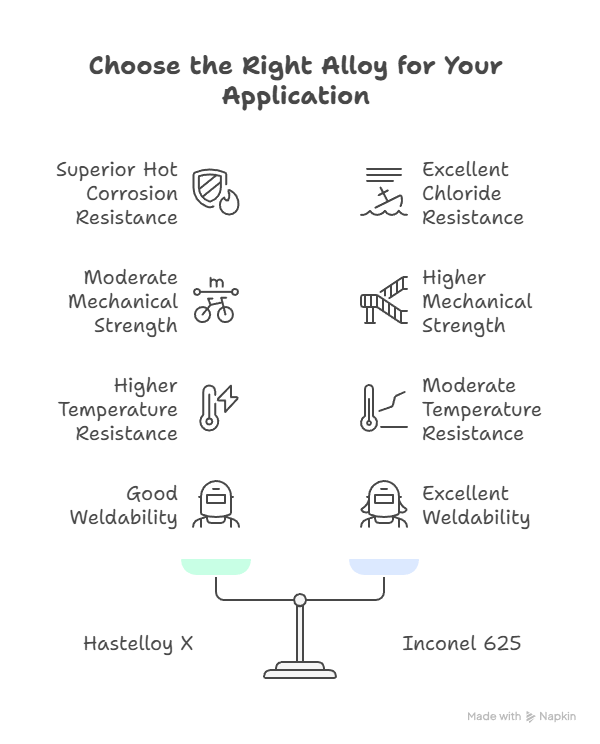
The differences in alloying elements influence corrosion resistance, high-temperature stability, and mechanical properties.
| Alloy | Nickel (Ni) | Chromium (Cr) | Molybdenum (Mo) | Iron (Fe) | Cobalt (Co) | Other Elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hastelloy X | 47–53% | 20–23% | 8–10% | 18–20% | 0–1% | C, Mn, Si, Fe minor |
| Inconel 625 | 58% min | 20–23% | 8–10% | 5% max | – | Niobium 3.15–4.15%, C trace |
Mechanical Properties Comparison
While both alloys maintain strength at high temperatures, Inconel 625 has higher tensile and yield strength due to niobium addition.
| Property | Hastelloy X | Inconel 625 |
|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 275–310 | 414–552 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 620–760 | 827–965 |
| Elongation (%) | 35–40 | 30–40 |
| Hardness (HRB) | 95–105 | 95–105 |
| Service Temperature (°C) | Up to 1200°C | Up to 980°C continuously |
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Both alloys resist high-temperature oxidation, but their chemical corrosion resistance differs.
| Environment | Hastelloy X | Inconel 625 |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidizing Atmosphere | Excellent at very high temperatures | Excellent up to 980°C |
| Hot Corrosive Chemicals | Superior, resists sulfidation and halide attack | Good, particularly in chloride environments |
| Marine / Seawater | Moderate resistance | Excellent resistance to chloride stress corrosion |
| High-Temperature Scaling | Excellent stability | Excellent |
Fabrication and Welding
Both alloys can be fabricated with care due to work hardening tendencies.
| Factor | Hastelloy X | Inconel 625 |
|---|---|---|
| Weldability | Good with nickel-based filler metals; preheating may be required | Excellent, widely used in welded assemblies |
| Formability | Moderate; work hardens at elevated temperatures | Good, but requires stress relief after heavy forming |
| Machinability | Moderate; sharp tools required | Moderate; slightly harder due to niobium strengthening |
Typical Applications
The choice depends on operating conditions such as chemical environment, temperature, and mechanical stress.
| Application Area | Hastelloy X | Inconel 625 |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Gas turbine combustion parts, furnace components | Turbine blades, exhaust components |
| Power Generation | Furnace components, heat exchangers, boiler tubes | Boiler tubes, heat exchangers, piping |
| Chemical Processing | Highly corrosive chemical vessels, heat exchangers | Chloride-resistant piping, reactors, valves |
| Marine / Offshore | High-temperature process equipment | Seawater piping, valves, desalination equipment |
Ncalloys Supply of High-Performance Alloys
Ncalloys supplies both Hastelloy X and Inconel 625 in bars, tubes, sheets, wires, and custom machined parts with full certification and quality assurance.
Manufacturer: Ncalloys
Contact Email: [email protected]
Related Questions
1. Which alloy is better for high-temperature chemical resistance?
Hastelloy X is superior in resisting hot corrosion and aggressive chemical environments.
2. Which alloy has higher mechanical strength?
Inconel 625 has higher tensile and yield strength due to niobium addition.
3. Can both alloys be welded?
Yes, both alloys are weldable with nickel-based filler metals, but Hastelloy X may require preheating for thick sections.



