Inconel 625 and Monel 400 are both nickel-based alloys widely used in marine, chemical, and industrial applications. While they share excellent corrosion resistance and durability, their chemical composition, mechanical strength, temperature capability, and ideal use cases are significantly different. Inconel 625 is a high-performance nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy designed for extreme environments, whereas Monel 400 is a nickel-copper alloy known for outstanding seawater resistance and cost efficiency.
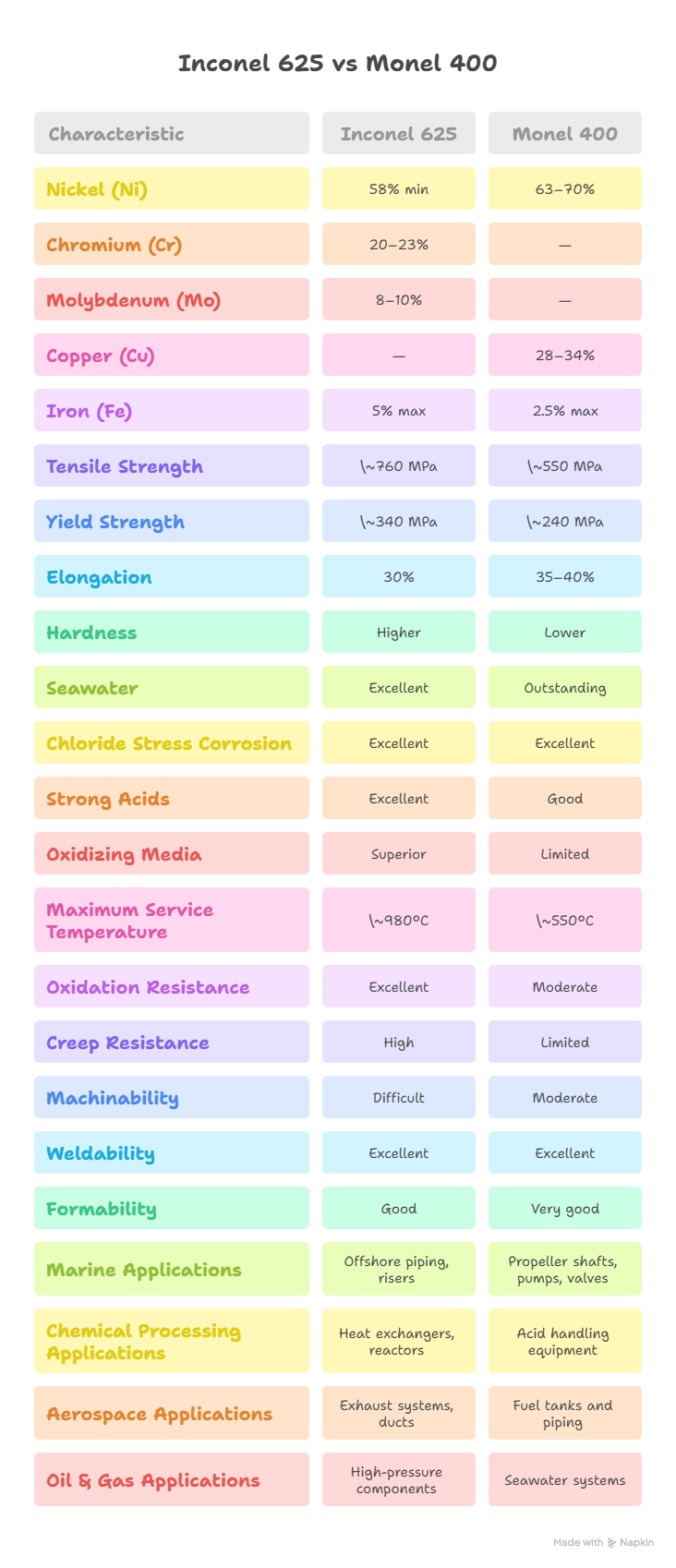
Chemical Composition Comparison
The difference in alloying elements directly affects corrosion behavior, strength, and temperature performance.
| Element | Inconel 625 | Monel 400 |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | 58% min | 63–70% |
| Chromium (Cr) | 20–23% | — |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 8–10% | — |
| Copper (Cu) | — | 28–34% |
| Iron (Fe) | 5% max | 2.5% max |
Mechanical Properties
Inconel 625 offers higher strength, especially at elevated temperatures, while Monel 400 focuses on toughness and ductility.
| Property | Inconel 625 | Monel 400 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | ~760 MPa | ~550 MPa |
| Yield Strength | ~340 MPa | ~240 MPa |
| Elongation | 30% | 35–40% |
| Hardness | Higher | Lower |
Corrosion Resistance
Both alloys are highly corrosion resistant, but they perform best in different environments.
| Environment | Inconel 625 | Monel 400 |
|---|---|---|
| Seawater | Excellent | Outstanding |
| Chloride Stress Corrosion | Excellent | Excellent |
| Strong Acids | Excellent | Good |
| Oxidizing Media | Superior | Limited |
Temperature Resistance
Inconel 625 is designed for much higher temperature service compared to Monel 400.
| Temperature Factor | Inconel 625 | Monel 400 |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Service Temperature | ~980°C | ~550°C |
| Oxidation Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Creep Resistance | High | Limited |
Machinability and Weldability
Both alloys are known for work hardening, but Monel 400 is generally easier to machine.
| Factor | Inconel 625 | Monel 400 |
|---|---|---|
| Machinability | Difficult | Moderate |
| Weldability | Excellent | Excellent |
| Formability | Good | Very good |
Typical Applications
Their performance differences determine where each alloy is most effective.
| Industry | Inconel 625 Applications | Monel 400 Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Marine | Offshore piping, risers | Propeller shafts, pumps, valves |
| Chemical Processing | Heat exchangers, reactors | Acid handling equipment |
| Aerospace | Exhaust systems, ducts | Fuel tanks and piping |
| Oil & Gas | High-pressure components | Seawater systems |
Cost Comparison
Material cost is often a deciding factor in alloy selection.
| Aspect | Inconel 625 | Monel 400 |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Processing Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Overall Cost Efficiency | Lower | Higher for marine use |
Which Alloy Should You Choose?
The choice depends on operating environment, temperature, and budget.
| Requirement | Recommended Alloy | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Seawater exposure | Monel 400 | Best-in-class seawater corrosion resistance |
| High temperature service | Inconel 625 | Designed for extreme heat and oxidation |
| Strong acidic environments | Inconel 625 | Chromium and molybdenum protection |
| Cost-sensitive projects | Monel 400 | Lower material and processing cost |
Related Questions
1. Is Inconel 625 better than Monel 400?
Inconel 625 is better for high-temperature and highly corrosive environments, while Monel 400 is superior in seawater applications.
2. Can Monel 400 replace Inconel 625?
Only in low-temperature, marine-focused applications where extreme heat and oxidation resistance are not required.
3. Which alloy is more expensive, Inconel 625 or Monel 400?
Inconel 625 is generally more expensive due to its complex alloying elements and higher performance capabilities.



