Monel 400 and Hastelloy C276 are two well-known nickel-based alloys widely used in corrosive and demanding industrial environments. Although both materials are valued for corrosion resistance, they are engineered for very different service conditions. Monel 400 is a nickel-copper alloy optimized for seawater and alkaline environments, while Hastelloy C276 is a nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy designed for extreme chemical corrosion, including strong acids and mixed corrosive media.
Chemical Composition Differences
The alloying elements define the fundamental performance gap between Monel 400 and Hastelloy C276.
| Element | Monel 400 | Hastelloy C276 |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | 63–70% | Balance |
| Copper (Cu) | 28–34% | — |
| Chromium (Cr) | — | 14.5–16.5% |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | — | 15–17% |
| Iron (Fe) | 2.5% max | 4–7% |
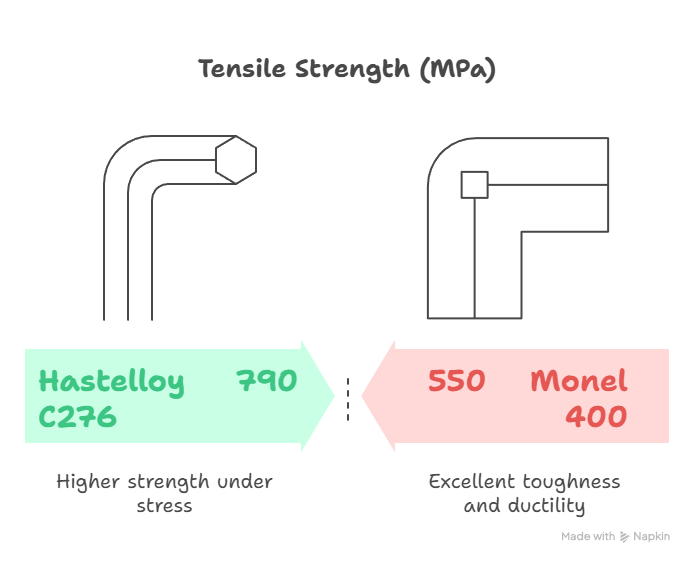
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Hastelloy C276 provides higher strength and better performance under severe stress, while Monel 400 offers excellent toughness and ductility.
| Property | Monel 400 | Hastelloy C276 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | ~550 MPa | ~790 MPa |
| Yield Strength | ~240 MPa | ~355 MPa |
| Elongation | 35–40% | 40% |
| Hardness | Lower | Higher |
Corrosion Resistance Performance
This is the most critical distinction between the two alloys.
| Corrosive Environment | Monel 400 | Hastelloy C276 |
|---|---|---|
| Seawater | Outstanding | Excellent |
| Hydrofluoric Acid | Excellent | Good |
| Sulfuric Acid | Good | Excellent |
| Hydrochloric Acid | Limited | Outstanding |
| Pitting & Crevice Corrosion | Moderate | Excellent |
Temperature Resistance
Hastelloy C276 is suitable for much higher operating temperatures than Monel 400.
| Temperature Factor | Monel 400 | Hastelloy C276 |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Service Temperature | ~550°C | ~1040°C |
| Oxidation Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Creep Resistance | Limited | High |
Fabrication and Machining
Both alloys are workable, but their processing characteristics differ.
| Aspect | Monel 400 | Hastelloy C276 |
|---|---|---|
| Machinability | Moderate | Difficult |
| Weldability | Excellent | Excellent |
| Cold Working | Very good | Good |
Typical Applications
The choice between Monel 400 and Hastelloy C276 depends largely on environmental severity.
| Industry | Monel 400 Applications | Hastelloy C276 Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Marine Engineering | Pump shafts, valves, fasteners | Seawater desalination components |
| Chemical Processing | Alkaline handling equipment | Reactors, heat exchangers |
| Oil & Gas | Seawater piping systems | Sour gas and acid service equipment |
| Pollution Control | — | Flue gas desulfurization systems |
Cost and Availability
Cost is a decisive factor for many engineering projects.
| Factor | Monel 400 | Hastelloy C276 |
|---|---|---|
| Material Cost | Lower | High |
| Processing Cost | Lower | High |
| Overall Cost Efficiency | High for marine use | High for extreme corrosion |
How to Choose Between Monel 400 and Hastelloy C276
Selecting the right alloy depends on corrosion type, temperature, and budget constraints.
| Requirement | Recommended Alloy | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Seawater and brine exposure | Monel 400 | Superior resistance to seawater corrosion |
| Strong acid environments | Hastelloy C276 | Exceptional resistance to mixed acids |
| High-temperature corrosion | Hastelloy C276 | Excellent oxidation and creep resistance |
| Cost-sensitive marine projects | Monel 400 | Lower material and fabrication cost |
Related Questions
1. Is Hastelloy C276 better than Monel 400?
Hastelloy C276 is better for extreme chemical and high-temperature environments, while Monel 400 excels in seawater and alkaline conditions.
2. Can Monel 400 replace Hastelloy C276?
Only in applications without strong acids or high temperatures, such as general marine and saltwater systems.
3. Which alloy is more expensive, Monel 400 or Hastelloy C276?
Hastelloy C276 is significantly more expensive due to its complex composition and superior corrosion resistance.



