A nickel alloy welding wire factory specializes in the production of high-performance filler materials used in welding applications that demand superior corrosion resistance, heat stability, and mechanical strength. Nickel-based welding wires are essential for joining nickel alloys, stainless steels, and dissimilar metals in industries such as petrochemical, aerospace, marine, and power generation. A professional factory ensures every wire meets strict metallurgical and dimensional requirements for consistent welding performance.
Overview of Nickel Alloy Welding Wires
Nickel alloy welding wires are designed to maintain high strength and corrosion resistance even in harsh environments such as seawater, acid solutions, and high-temperature oxidation zones. These wires are available in both solid and flux-cored forms, depending on the application and welding process. The most common grades include Inconel 625, Inconel 718, Monel 400, and Hastelloy C-276.
| Welding Wire Type | Main Composition | Typical Use | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
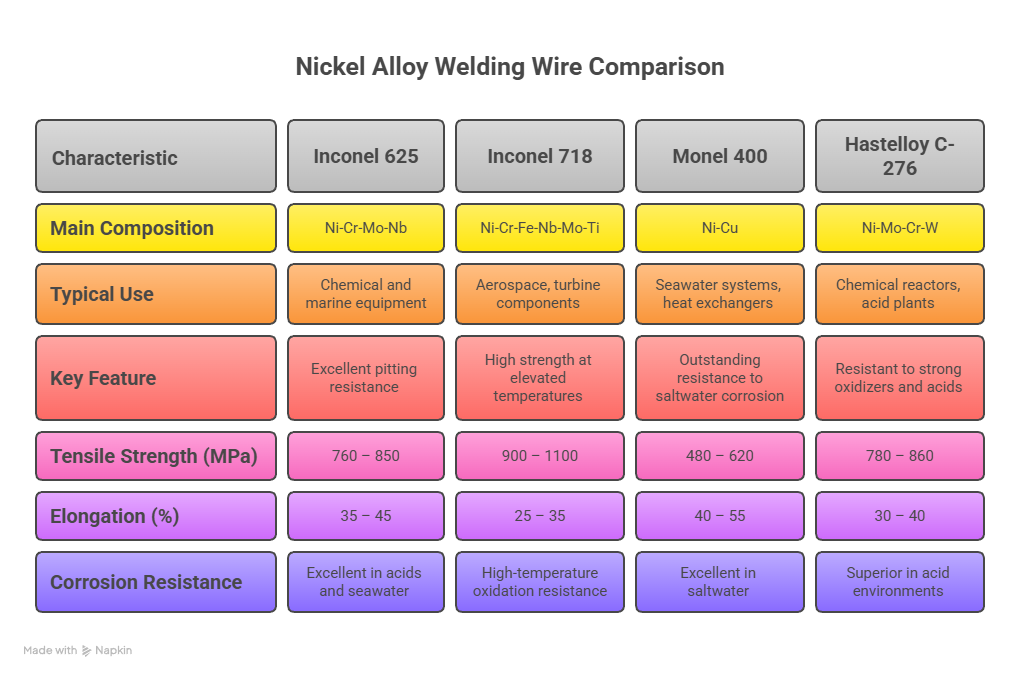
| Inconel 625 | Ni-Cr-Mo-Nb | Chemical and marine equipment | Excellent pitting resistance |
| Inconel 718 | Ni-Cr-Fe-Nb-Mo-Ti | Aerospace, turbine components | High strength at elevated temperatures |
| Monel 400 | Ni-Cu | Seawater systems, heat exchangers | Outstanding resistance to saltwater corrosion |
| Hastelloy C-276 | Ni-Mo-Cr-W | Chemical reactors, acid plants | Resistant to strong oxidizers and acids |
Manufacturing Process in a Nickel Alloy Welding Wire Factory
The manufacturing process of nickel alloy welding wire requires precision metallurgy and advanced equipment to ensure consistent chemical composition and mechanical properties. Every step, from melting to drawing, is controlled to meet international standards such as AWS A5.14, ASTM B166, and ISO 18274.
| Stage | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Melting | High-purity nickel and alloying elements are melted in a vacuum induction furnace | Ensure homogenous alloy structure |
| 2. Casting | Molten metal is cast into billets or rods | Prepare material for wire drawing |
| 3. Hot Rolling | Billets are rolled into wire rods | Reduce cross-section while maintaining ductility |
| 4. Annealing | Intermediate heat treatment | Enhance flexibility and reduce stress |
| 5. Pickling | Surface cleaning with acid solution | Remove oxide scales and impurities |
| 6. Wire Drawing | Continuous reduction through dies | Achieve precise wire diameters |
| 7. Spooling | Coiling onto spools or drums | Prepare for shipment or welding automation |
| 8. Testing | Chemical, mechanical, and NDT verification | Ensure compliance with specifications |
Nickel Alloy Welding Wire Grades and Their Properties
Different nickel alloy grades provide unique combinations of strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability. The selection of the proper welding wire depends on the base material, welding environment, and service condition.
| Grade | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERNiCrMo-3 (Inconel 625) | 760 – 850 | 35 – 45 | Excellent in acids and seawater |
| ERNiCr-3 (Inconel 82) | 690 – 760 | 30 – 40 | Good for dissimilar welding |
| ERNiCrFe-7 (Inconel 718) | 900 – 1100 | 25 – 35 | High-temperature oxidation resistance |
| ERNiCu-7 (Monel 400) | 480 – 620 | 40 – 55 | Excellent in saltwater |
| ERNiCrMo-4 (Hastelloy C-276) | 780 – 860 | 30 – 40 | Superior in acid environments |
Applications of Nickel Alloy Welding Wires
Nickel alloy welding wires are widely used in environments where corrosion, heat, and mechanical stress are severe. Their adaptability makes them suitable for various welding techniques, including GTAW (TIG), GMAW (MIG), and SAW (submerged arc welding).
| Industry | Application | Reason for Use |
|---|---|---|
| Petrochemical | Heat exchangers, reactors, piping systems | Excellent resistance to acid and chloride corrosion |
| Power Generation | Boiler tubes, turbine casings | High-temperature strength |
| Marine Engineering | Seawater pumps, offshore rigs | Chloride stress corrosion resistance |
| Aerospace | Jet engines, exhaust systems | High fatigue and oxidation resistance |
| Chemical Processing | Acid towers, scrubbers | Stable in reducing and oxidizing media |
Quality Control and Testing
Every nickel alloy welding wire undergoes a series of inspections to ensure it meets the necessary metallurgical and performance standards. Factories follow ISO, AWS, and ASTM protocols to guarantee quality consistency and welding stability.
| Test | Standard | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | ASTM E1473 | Verify alloy chemistry |
| Tensile Testing | ASTM E8 | Confirm mechanical strength |
| Microstructure Analysis | ASTM E3 | Check grain size and phase uniformity |
| Surface Inspection | Visual + Eddy Current | Detect cracks and inclusions |
| Dimensional Check | ISO 16120 | Ensure correct wire diameter |
Advantages of Choosing a Professional Nickel Alloy Welding Wire Factory
Choosing an experienced nickel alloy welding wire factory ensures superior product consistency, customized grades, and full documentation. Many factories are certified under ISO 9001, CE, and PED systems, guaranteeing reliability for global clients.
| Factory Feature | Advantage | Customer Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Melting | Low impurity level | Improved weld purity |
| Precision Drawing Machines | Uniform diameter tolerance | Smooth wire feeding |
| Automated Annealing Furnaces | Consistent mechanical properties | Reliable welding results |
| Comprehensive Testing Lab | 100% quality inspection | Guaranteed compliance |
| Global Export Experience | Standard packaging and logistics | Fast worldwide delivery |
Packing and Shipping Standards
Nickel alloy welding wires are packed with great care to prevent contamination, oxidation, and mechanical damage. Depending on the customer’s requirements, wires are supplied in different spool sizes or bulk drums, sealed, and labeled for traceability.
| Packing Type | Capacity | Protection | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Spool | 5 – 15 kg | Dust and moisture protection | Manual welding |
| Metal Drum | 100 – 250 kg | Strong mechanical protection | Automated welding |
| Vacuum Sealed Bag | Variable | Prevents oxidation | Long-term storage |
| Wooden Crate | Custom | Export shipment | Overseas delivery |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between solid and flux-cored nickel alloy welding wires?
Solid wires are typically used for TIG and MIG welding where cleanliness and precision are critical. Flux-cored wires contain internal flux for shielding, allowing for higher deposition rates and easier welding in outdoor or high-wind environments.
2. Which industries use nickel alloy welding wires most frequently?
Nickel alloy welding wires are primarily used in chemical processing, marine, aerospace, and power generation industries where corrosion resistance and heat stability are essential for safety and longevity.
3. What standards do nickel alloy welding wires follow?
Factories generally manufacture according to AWS A5.14, ASTM B166, and ISO 18274 standards, ensuring compliance with mechanical strength, chemical composition, and weldability specifications.



