A nickel welding rod factory specializes in producing high-quality filler rods for welding applications that require exceptional corrosion resistance, heat tolerance, and mechanical strength. Nickel welding rods are critical in industries like chemical processing, aerospace, marine engineering, and power generation. A professional factory ensures precise alloy composition, strict quality control, and consistent rod dimensions to provide reliable welding performance for demanding environments.
Overview of Nickel Welding Rods
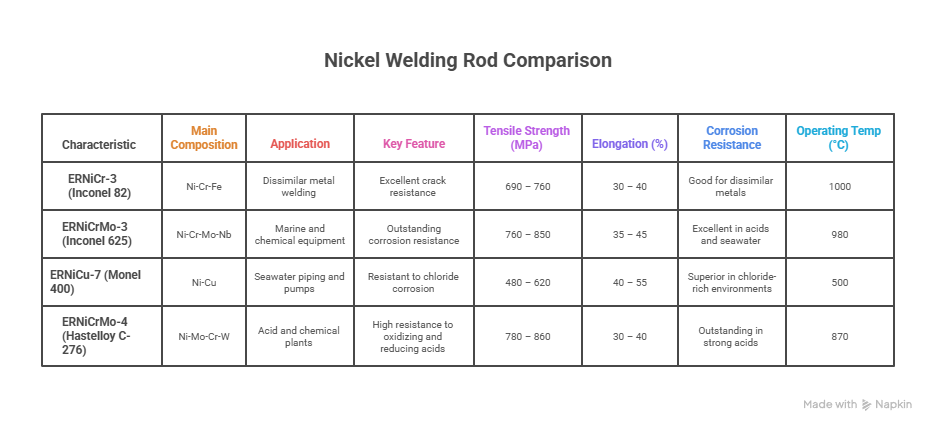
Nickel welding rods are primarily used for joining nickel alloys, stainless steels, and other high-performance metals. They are available in various diameters and grades, each designed to handle specific temperature ranges, chemical exposures, and mechanical stresses. Common nickel rod grades include ERNiCr-3 (Inconel 82), ERNiCrMo-3 (Inconel 625), ERNiCu-7 (Monel 400), and ERNiCrMo-4 (Hastelloy C-276).
| Rod Grade | Main Composition | Application | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERNiCr-3 (Inconel 82) | Ni-Cr-Fe | Dissimilar metal welding | Excellent crack resistance |
| ERNiCrMo-3 (Inconel 625) | Ni-Cr-Mo-Nb | Marine and chemical equipment | Outstanding corrosion resistance |
| ERNiCu-7 (Monel 400) | Ni-Cu | Seawater piping and pumps | Resistant to chloride corrosion |
| ERNiCrMo-4 (Hastelloy C-276) | Ni-Mo-Cr-W | Acid and chemical plants | High resistance to oxidizing and reducing acids |
Manufacturing Process of Nickel Welding Rods
The production of nickel welding rods involves precise alloying, hot working, annealing, and surface finishing to achieve consistent performance. Quality control is maintained throughout every stage to meet AWS, ASTM, and ISO standards.
| Stage | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Alloy Melting | High-purity nickel and alloying elements are melted in vacuum or induction furnaces | Ensure homogenous composition |
| 2. Casting | Molten metal cast into billets or rods | Prepare for rolling and drawing |
| 3. Hot Rolling | Billets rolled into rod form | Reduce diameter while maintaining ductility |
| 4. Annealing | Heat treatment to relieve stress | Enhance flexibility and weldability |
| 5. Surface Cleaning | Pickling or descaling | Remove oxidation for clean welding |
| 6. Cutting and Straightening | Rods cut to standard lengths and straightened | Ease of handling and welding |
| 7. Quality Testing | Chemical, mechanical, and dimensional verification | Ensure compliance with specifications |
| 8. Packaging | Rod bundles packed in moisture-resistant boxes or tubes | Prevent damage and oxidation |
Mechanical and Chemical Properties
Nickel welding rods are engineered to provide high tensile strength, ductility, and excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation. Properties vary by alloy type to match the service requirements of the base metals being welded.
| Property | ERNiCr-3 | ERNiCrMo-3 | ERNiCu-7 | ERNiCrMo-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 690 – 760 | 760 – 850 | 480 – 620 | 780 – 860 |
| Elongation (%) | 30 – 40 | 35 – 45 | 40 – 55 | 30 – 40 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good for dissimilar metals | Excellent in acids and seawater | Superior in chloride-rich environments | Outstanding in strong acids |
| Operating Temp (°C) | 1000 | 980 | 500 | 870 |
Applications of Nickel Welding Rods
Nickel welding rods are used extensively in industries where corrosion, high temperature, or mechanical stress is critical. They provide reliable joints for demanding applications.
| Industry | Application | Reason for Use |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Reactors, heat exchangers | Resistance to acids and corrosive media |
| Marine Engineering | Seawater piping, pumps | Chloride and saltwater resistance |
| Aerospace | Engines, exhaust ducts | High-temperature strength and oxidation resistance |
| Power Generation | Boiler tubes, turbines | Heat and corrosion resistance |
| Oil & Gas | Sour gas pipelines, risers | Resistance to sulfide stress cracking |
Quality Control in a Nickel Welding Rod Factory
High-quality nickel welding rods require rigorous testing to ensure compliance with international standards. Factories employ chemical analysis, tensile testing, microstructure examination, and surface inspections to guarantee reliability.
| Test | Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Spectrometer or wet analysis | Verify alloy consistency |
| Tensile & Yield Strength | ASTM E8 | Ensure mechanical performance |
| Microstructure | Optical or SEM analysis | Check for defects or segregation |
| Surface Inspection | Visual and eddy current | Detect cracks, porosity, or inclusions |
| Dimensional Check | Calipers and gauges | Confirm rod diameter and length |
Packing and Shipping Standards
Nickel welding rods are packed to prevent oxidation and mechanical damage during storage and shipment. Common packing methods include moisture-resistant boxes, sealed tubes, and wooden crates for international shipping. Each package comes with full documentation including chemical certificates and heat numbers.
| Packing Type | Protection | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Sealed Tube | Prevents oxidation | Domestic and export use |
| Cardboard Box with Desiccant | Moisture control | Short-term storage |
| Wooden Crate | Mechanical protection for bulk shipment | International shipping |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between ERNiCr-3 and ERNiCrMo-3 rods?
ERNiCr-3 (Inconel 82) is mainly used for dissimilar metal welding and offers good corrosion resistance, while ERNiCrMo-3 (Inconel 625) provides superior corrosion resistance, especially in acidic and seawater environments, and is suitable for high-performance applications.
2. Can nickel welding rods be used in high-temperature applications?
Yes. Depending on the alloy grade, nickel welding rods can operate at temperatures up to 1000°C, providing excellent strength, oxidation resistance, and durability in high-temperature environments.
3. What standards ensure the quality of nickel welding rods?
Nickel welding rods are typically manufactured according to AWS A5.14, ASTM BNi-2/BNi-7, and ISO 18274 standards, which ensure proper chemical composition, mechanical properties, and weldability for industrial applications.



