Nimonic 90 and Inconel are both high-performance nickel-based superalloys widely used in aerospace, power generation, and high-temperature engineering. While they share similarities such as excellent strength at elevated temperatures and resistance to oxidation, their alloy design philosophy, strengthening mechanisms, and typical applications are different. Nimonic 90 is a precipitation-hardened alloy optimized for extreme high-temperature strength, whereas Inconel represents a broader family of nickel-chromium alloys designed for a balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and fabrication flexibility.
Alloy Family Overview
Nimonic 90 is a nickel-chromium-cobalt alloy strengthened by gamma prime precipitation through aluminum and titanium additions. It is specifically developed for high-stress, high-temperature rotating components.
Inconel refers to a family of nickel-chromium-based alloys, such as Inconel 600, 625, 718, and 750, each optimized for different combinations of corrosion resistance, strength, and temperature capability.
Chemical Composition Comparison
| Element | Nimonic 90 | Typical Inconel Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | Balance | Balance |
| Chromium (Cr) | 18 – 21% | 15 – 23% |
| Cobalt (Co) | 15 – 21% | — |
| Aluminum (Al) | 1 – 1.8% | 0 – 1.5% |
| Titanium (Ti) | 2 – 3% | 0 – 5% |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | — | 0 – 9% |
The high cobalt, aluminum, and titanium content in Nimonic 90 provides exceptional precipitation hardening, while many Inconel grades rely on solid solution strengthening or combined mechanisms.
Strengthening Mechanism
Nimonic 90 is primarily strengthened through gamma prime precipitation, which provides excellent tensile, fatigue, and creep strength at very high temperatures.
Inconel alloys may use solid solution strengthening (such as Inconel 625) or precipitation hardening (such as Inconel 718), depending on the grade.
Mechanical Properties
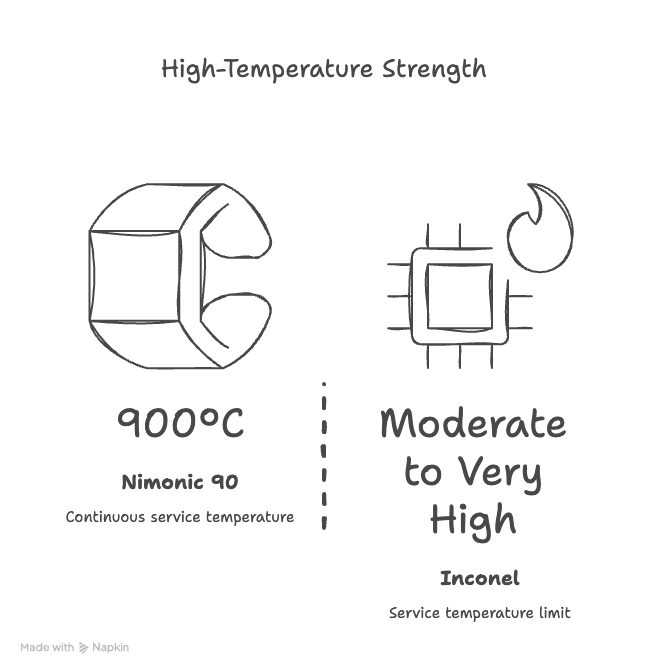
Nimonic 90 offers extremely high tensile strength and creep resistance at temperatures up to approximately 900°C, making it suitable for highly stressed components.
Inconel alloys provide a wider range of mechanical performance, with some grades optimized for weldability and corrosion resistance rather than maximum strength.
| Property | Nimonic 90 | Inconel (Typical Range) |
|---|---|---|
| Room Temperature Strength | Very High | Moderate to High |
| High-Temperature Strength | Excellent | Good to Excellent |
| Creep Resistance | Outstanding | Moderate to High |
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Nimonic 90 provides good oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures but is not primarily designed for aggressive chemical corrosion environments.
Inconel alloys generally offer superior corrosion resistance in a wide range of chemical environments, especially grades containing molybdenum.
Temperature Capability
Nimonic 90 is typically used at continuous service temperatures up to about 900°C in highly stressed conditions.
Inconel alloys have service temperature limits ranging from moderate to very high, depending on the specific grade and application.
Fabrication and Machinability
Nimonic 90 is difficult to machine and form due to its high strength and work-hardening characteristics. Precision manufacturing processes are often required.
Inconel alloys generally offer better fabrication flexibility, especially grades like Inconel 625 and 600.
Typical Applications
Nimonic 90 Applications:
Turbine blades, turbine discs, exhaust valves, aerospace fasteners, and high-temperature rotating components.
Inconel Applications:
Heat exchangers, aerospace structures, chemical processing equipment, oil and gas components, fasteners, and high-temperature piping.
Cost Comparison
Nimonic 90 is generally more expensive due to its cobalt content and complex heat treatment requirements.
Inconel pricing varies by grade, with some corrosion-resistant grades offering a more economical solution.
How to Choose Between Nimonic 90 and Inconel
Choose Nimonic 90 if: the application demands maximum strength, fatigue resistance, and creep performance at extreme temperatures.
Choose Inconel if: a balance of corrosion resistance, weldability, and cost efficiency is required.
Related Questions
Is Nimonic 90 stronger than Inconel?
Yes, Nimonic 90 generally offers higher strength at elevated temperatures compared to most Inconel grades.
Which is better for corrosion resistance, Nimonic 90 or Inconel?
Inconel alloys typically provide better corrosion resistance in chemical environments.
Can Inconel replace Nimonic 90 in turbine applications?
Only certain high-strength Inconel grades can be considered, but Nimonic 90 remains preferred for extreme high-temperature stress.



