Inconel is a family of nickel-chromium-based superalloys designed for high strength, excellent oxidation resistance, and outstanding performance in extreme environments. These alloys are widely used in aerospace, chemical processing, power generation, and marine industries because they maintain their mechanical properties even at very high temperatures and resist corrosion in harsh chemical environments.
Definition of Inconel
Inconel refers to a group of high-performance alloys primarily composed of nickel (Ni) and chromium (Cr), often with iron (Fe), molybdenum (Mo), cobalt (Co), and other elements added to enhance specific properties. The key feature of Inconel is its ability to retain strength and resist oxidation and corrosion under extreme conditions such as high temperatures, acidic environments, or high-stress applications.
Chemical Composition of Inconel Alloys
The exact composition depends on the specific grade, but typical elements include:
| Element | Typical Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | 50–76 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 14–23 |
| Iron (Fe) | 5–15 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 2–7 |
| Cobalt (Co) | ≤1 |
| Carbon (C) | 0.1 max |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤1 |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤0.5 |
These elements create a stable, corrosion-resistant alloy capable of withstanding aggressive chemical environments and high temperatures up to 1000°C or more, depending on the grade.
Main Properties of Inconel
Inconel alloys possess multiple key properties that make them suitable for critical applications:
High Temperature Strength
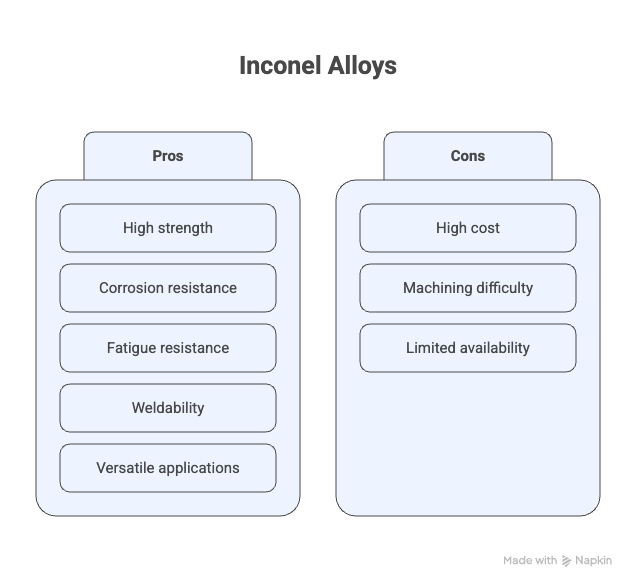
Inconel retains its mechanical strength at elevated temperatures where most steels and other alloys would weaken. This makes it ideal for turbine blades, exhaust systems, and furnace components.
Oxidation and Corrosion Resistance
Due to its high chromium and nickel content, Inconel forms a stable, protective oxide layer on the surface, resisting oxidation and corrosion from acids, alkalis, and seawater.
Fatigue and Creep Resistance
Inconel exhibits excellent fatigue resistance under cyclic loads and maintains stability over long periods at high temperatures (creep resistance), making it suitable for jet engines, nuclear reactors, and chemical plants.
Weldability and Fabrication
Inconel can be welded using conventional methods, including TIG and MIG. It is also available in forms such as sheets, plates, bars, tubes, and wires, allowing versatile manufacturing for industrial and aerospace components.
Common Inconel Grades
Several grades are tailored for specific applications:
| Grade | Special Features |
|---|---|
| Inconel 600 | Excellent oxidation and corrosion resistance; suitable for chemical processing and heat treatment applications |
| Inconel 625 | High strength, outstanding corrosion resistance, ideal for aerospace and marine applications |
| Inconel 718 | Precipitation-hardened alloy, extremely high strength at elevated temperatures, widely used in jet engines |
| Inconel 601 | Oxidation and heat resistance, used in furnace parts and chemical equipment |
Applications of Inconel
Due to its combination of high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance, Inconel is widely used in demanding environments:
Aerospace: Turbine blades, jet engine components, exhaust systems
Chemical Processing: Heat exchangers, reactors, chemical tanks, piping
Marine: Seawater valves, pump shafts, desalination equipment
Power Generation: Nuclear reactor components, furnace parts, steam turbines
Oil & Gas: Downhole equipment, high-pressure valves, and pipelines
Why Choose Inconel
Engineers select Inconel when materials are required to perform under high temperatures, corrosive environments, or cyclic stress conditions. Its unique nickel-chromium composition ensures reliability, durability, and minimal maintenance, which makes it a top choice in industries where failure is not an option.
Related Questions
What is Inconel used for?
Inconel is used in aerospace engines, chemical processing plants, marine equipment, power generation, and oil & gas applications due to its high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance.
Is Inconel stronger than stainless steel?
Yes, Inconel generally offers superior high-temperature strength, creep resistance, and corrosion resistance compared to most stainless steels.
Can Inconel be welded?
Yes, Inconel can be welded using standard methods such as TIG and MIG, but specialized techniques are recommended to prevent cracking and maintain mechanical properties.



