Inconel is a family of high-performance nickel-based superalloys primarily made of nickel combined with chromium and other alloying elements such as molybdenum, iron, niobium, and cobalt. These elements are carefully balanced to give Inconel exceptional resistance to high temperature, oxidation, corrosion, and mechanical stress. Because of this unique composition, Inconel is widely used in aerospace, oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation industries.
Main Elements in Inconel Alloys
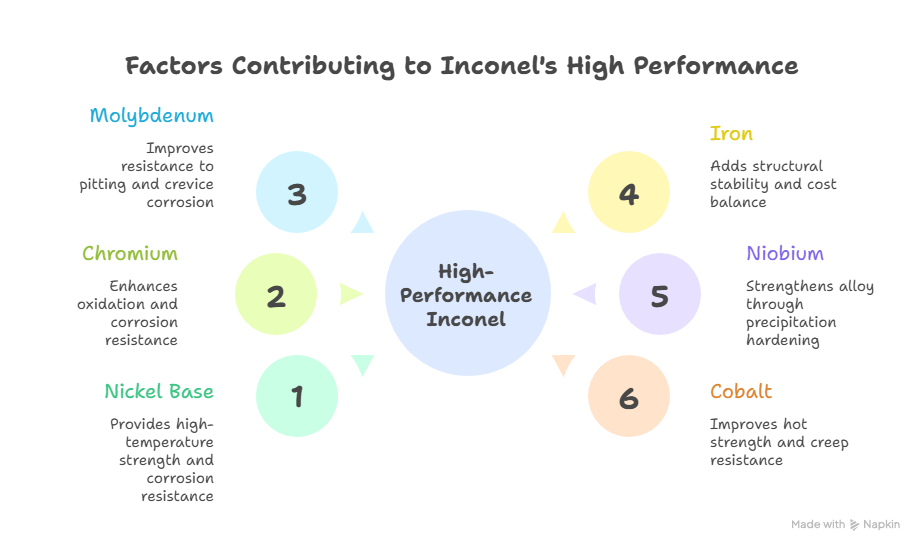
The core composition of Inconel alloys is based on nickel, with additional elements added to enhance specific properties.
| Element | Typical Role in Inconel |
|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | Base element providing high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance |
| Chromium (Cr) | Improves oxidation and corrosion resistance |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Enhances resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion |
| Iron (Fe) | Adds structural stability and cost balance |
| Niobium (Nb) | Strengthens alloy through precipitation hardening |
| Cobalt (Co) | Improves hot strength and creep resistance |
Typical Chemical Composition of Common Inconel Grades
Different Inconel grades are engineered for specific operating environments by adjusting alloying elements.
| Inconel Grade | Main Alloying Elements |
|---|---|
| Inconel 600 | Nickel, chromium, iron |
| Inconel 625 | Nickel, chromium, molybdenum, niobium |
| Inconel 718 | Nickel, chromium, iron, niobium, molybdenum |
| Inconel X-750 | Nickel, chromium, titanium, aluminum |
Why Nickel Is the Base of Inconel
Nickel forms the foundation of Inconel alloys because it maintains strength and stability at extremely high temperatures where many other metals fail.
| Nickel Property | Benefit in Inconel |
|---|---|
| High Melting Point | Allows use in high-temperature environments |
| Corrosion Resistance | Protects against acids, alkalis, and seawater |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains mechanical properties under heat |
| Alloy Compatibility | Easily combines with chromium, molybdenum, and iron |
Role of Chromium in Inconel
Chromium is a key alloying element that enables Inconel to resist oxidation and scaling at elevated temperatures.
| Chromium Function | Performance Impact |
|---|---|
| Oxide Layer Formation | Creates a protective surface film |
| Corrosion Resistance | Improves resistance to oxidizing environments |
| High-Temperature Stability | Reduces surface degradation |
Strengthening Elements in Inconel
Inconel alloys achieve their exceptional strength through solid-solution and precipitation strengthening mechanisms.
| Element | Strengthening Effect |
|---|---|
| Molybdenum | Solid-solution strengthening and corrosion resistance |
| Niobium | Precipitation hardening for high yield strength |
| Aluminum & Titanium | Formation of strengthening precipitates |
How Inconel Composition Affects Applications
The combination of nickel, chromium, and strengthening elements allows Inconel to perform where standard stainless steels and alloys fail.
| Application Requirement | Compositional Advantage |
|---|---|
| High-temperature service | Nickel-rich matrix maintains strength |
| Oxidizing environments | Chromium protects against scaling |
| Severe corrosion | Molybdenum and chromium resist pitting |
| High mechanical stress | Niobium and precipitation strengthening |
Inconel Materials Supplied by Ncalloys
Ncalloys supplies a full range of Inconel materials including bars, plates, tubes, wires, and forgings. Our Inconel products are manufactured with strict chemical control and full material traceability to meet demanding industrial standards.
Manufacturer: Ncalloys
Contact Email: [email protected]
Related Questions
1. Is Inconel made of pure nickel?
No, Inconel is not pure nickel. It is a nickel-based alloy that includes chromium and other elements to enhance strength and corrosion resistance.
2. Why does Inconel contain chromium?
Chromium improves oxidation resistance and protects the alloy from scaling and corrosion at high temperatures.
3. Does Inconel contain iron?
Yes, many Inconel grades contain iron to improve structural stability and reduce material cost while maintaining performance.



